This knowledge article will help you understand the difference between Delegated permissions and Application permissions when integrating DatabeatOMNI with Microsoft 365.
If you plan to integrate DatabeatOMNI with your Microsoft 365 tenant, it's essential to have a good understanding of how Microsoft 365 permissions work. This knowledge article is designed to help you get a better grasp of it. Keep in mind that Microsoft has a wealth of documentation on this topic, and your organization's Microsoft 365 tenant, internal security policies, and IT department will ultimately make the decisions and set limitations.
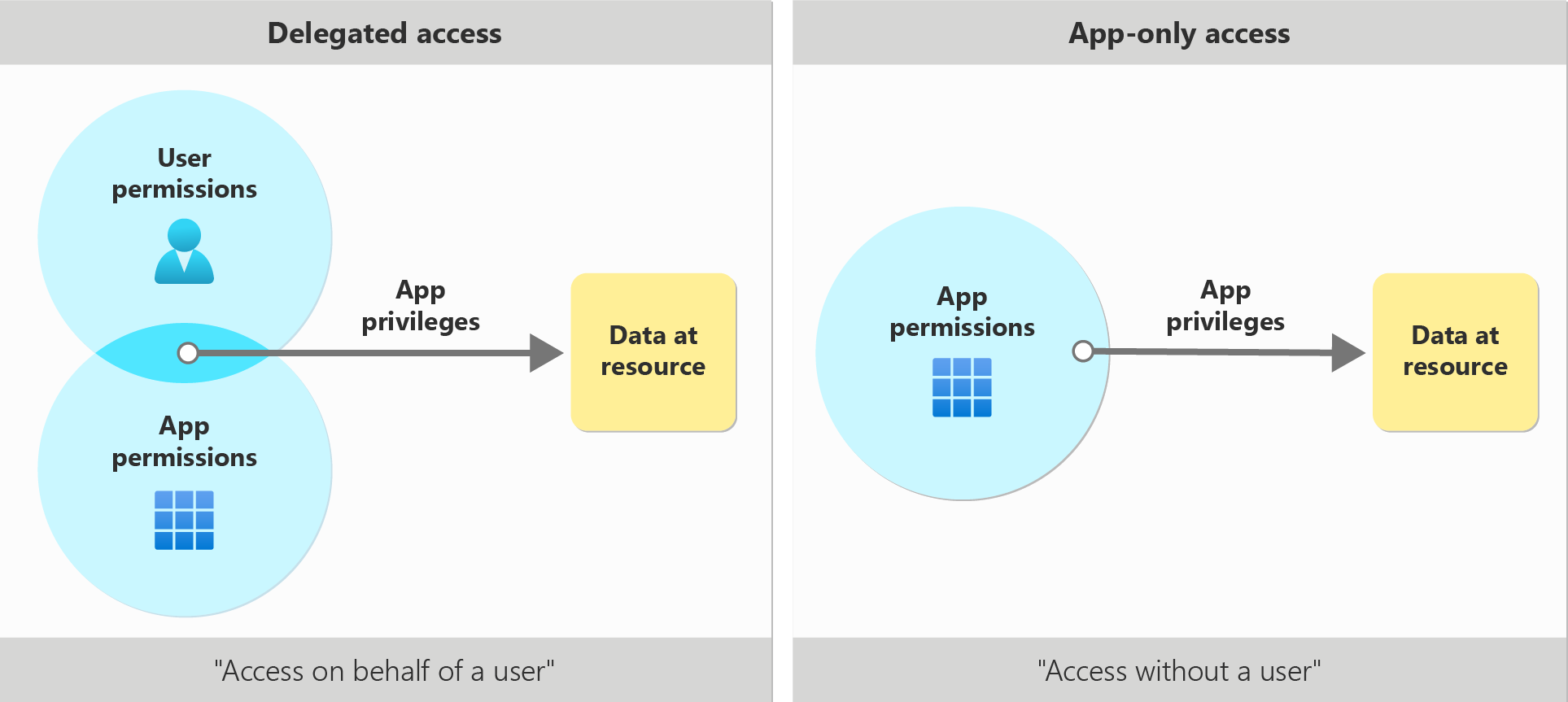
In short, delegated permissions are permissions granted to applications like DatabeatOMNI to perform specific tasks on behalf of a user.
On the other hand, application permissions are granted to applications themselves, allowing the application to access and perform broader actions within the Microsoft 365 environment, without the need for a logged-in user.
Microsoft can help visualise this concept and explain more on learn.microsoft.com:
Learn more here: Introduction to permissions and consentSource: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/active-directory/develop/permissions-consent-overview#access-scenarios
Delegated permissions
Application permissions
In contrast to delegated permissions, application permissions are granted to an application itself rather than acting on behalf of a specific user.
For example, if your organization is using Databeat Doorsign to allow touch booking on touch screens outside meeting rooms it is likely that application permissions come into play to simplify your day.
When you touch the display and book a 30 min meeting right there on the spot, DatabeatOMNI will manage this for you. You won't need to sign in with your Microsoft 365 account every time because it DatabeatOMNI has the application permission "Read and Write all calendar Mailboxes" and can book the room for you - without the need for individual user authentication.
When an AAD enterprise application is granted application permissions, it gains broader access and capabilities within the Microsoft 365 environment. These permissions are not tied to any individual user's identity. These permissions may allow the DatabeatOMNI - Business enterprise application to perform tasks and access resources independently, without requiring user authentication.
It's important to note that application permissions should be carefully managed and granted only to trusted applications, as they have the potential to access sensitive data and perform actions across the entire organization.
Restricting application permissions
DatabeatOMNI should not be allowed to book all calendars in your organization, but only the specific resource calendars you want it to book. To restrict the application permissions given to the DatabeatOMNI - Business app you can create internal policies, only allowing specific calendars or a group of resources to be booked by DatabeatOMNI. If this seems relevant, then check out the article: How to restrict DatabeatOMNI's application permissions.
Managing your DatabeatOMNI - Business Enterprise Application
As a Microsoft 365 tenant administrator, you can check out the Microsoft Entra admin center (AAD admin portal) to review your organization's current settings and policies for the "DatabeatOMNI - Business" enterprise application.
The app is registered as an enterprise application called "DatabeatOMNI - Business" located under Applications/Enterprise applications/DatabeatOMNI - Business.